Combined Bending and Axial Compression
Cross-sectional Inputs
All references to EN 1995-1-1:2004 unless otherwise stated.
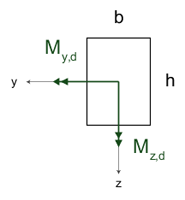
This tests a cross-section in combined compression parallel to the grain and biaxial bending around the y-y and z-z axes according to Clause 6.2.4.
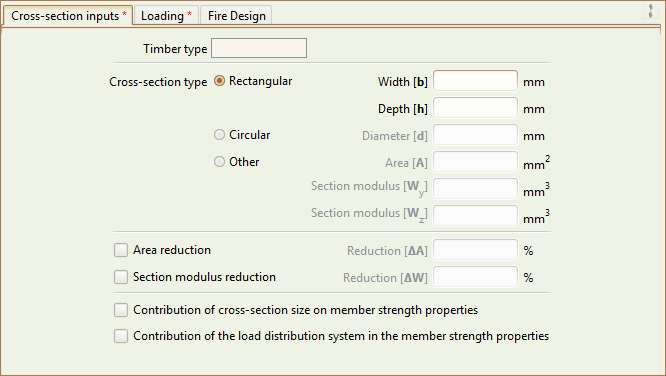
Timber type
The timber type of the cross-section. See the timber database section for the types supported by Teretron.
Cross-section type
The geometry type of the cross-section.
Width bThe width of a rectangular cross-section, in mm. Depth hThe depth of a rectangular cross-section, in mm. |
|
|
Diameter dThe diameter of a circular cross-section, in mm. |

|
Area A
The area of a generic cross-section, in mm2.
Section modulus Wy
The section modulus of the cross-section about the y-y axis, in mm3.
Section modulus Wz
The section modulus of the cross-section about the z-z axis, in mm3.
Area reduction
The area reduction ΔA refers to reductions in the nominal cross-section size that have to be taken into account in the calculation of the member strength (e.g. holes from fasteners) according to Subclause 5.2(2).
It should be given as a percentage of the total nominal area of the cross-section.
Section modulus reduction
The section modulus reduction ΔW refers to reductions in the nominal cross-sectional modulus that are to be taken into account in the calculation of the member strength (e.g. holes from fasteners) according to Subclause 5.2(2).
It should be given as a percentage of the total nominal section modulus of the cross-section.
Contribution of cross-section size on the determination of member strength properties
Includes factors kh for the calculation of the member strength in solid timber, glulam and LVL, according to Clauses 3.2, 3.3, and 3.4.
Contribution of the load distribution system in the member strength properties
Includes factor ksys for the calculation of the member strength, according to Clause 6.6, for a member that functions as part of a continuous load distribution system.
Note that Subclause 6.6(3) states that the strength verification for a continuous load distribution system should be carried out assuming short-term load duration.
